How Fast Can an Electric Car Charge? The charging duration of an electric car (EV) varies significantly with charger types, the battery capacity of the vehicle, and several other deciding factors. Charging duration can range from 15–30 minutes for quick charging to over 24 hours for slow charging. EV owners must understand these options to schedule charging and minimize downtime.
Charging an EV isn’t a case of refuelling a traditional car simply—charging entails supplying a car with variable amounts of power, according to charging infrastructure and a car’s capabilities. There are charging methodologies ideal for overnight at-home recharging, and then recharging for extended trips at a rapid pace. How convenient and rapidly an EV can be recharged is partially determined by charging infrastructure availability
Current EVs possess advanced battery management systems that regulate charging speed for battery longevity. The majority of charging systems slow down when the battery is at 80% capacity in an effort to prevent overheating and reduce battery cell wear and tear. What that means is that even if initial charging is fast, filling up the last 20% of the battery will be slow.
To understand an EV’s charging speed, one must see the types of charging options, from a humble household outlet to high-powered DC Fast Chargers. All have a variety of speeds, and each is ideal for a specific use case.
Types and Charging Rates of EV Chargers
Among the most important factors in charging speed is charger type. There are three key levels of EV charging, and they have different power output and charging times.
Level 1 Charging (Domestic Outlet
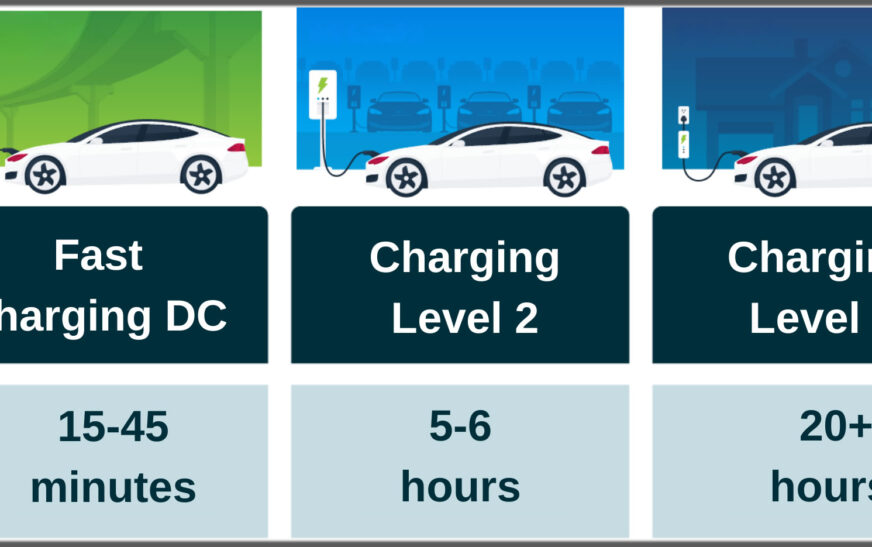
Level 1 charging uses a standard 120-volt household outlet and is the slowest of the three charging options. It adds typically 3 to 5 miles of range per hour and is best suited for overnight charging of plug-in hybrid vehicles (PHEVs) or EVs with small battery packs. A fully electric vehicle equipped with a 60 kWh battery would take over 24 hours to fully charge this way. While Level 1 charging can be convenient for drivers who don’t drive very far each day, it’s not practical for drivers who require faster recharging.
Level 2 Charging (Home and Public Charging Station
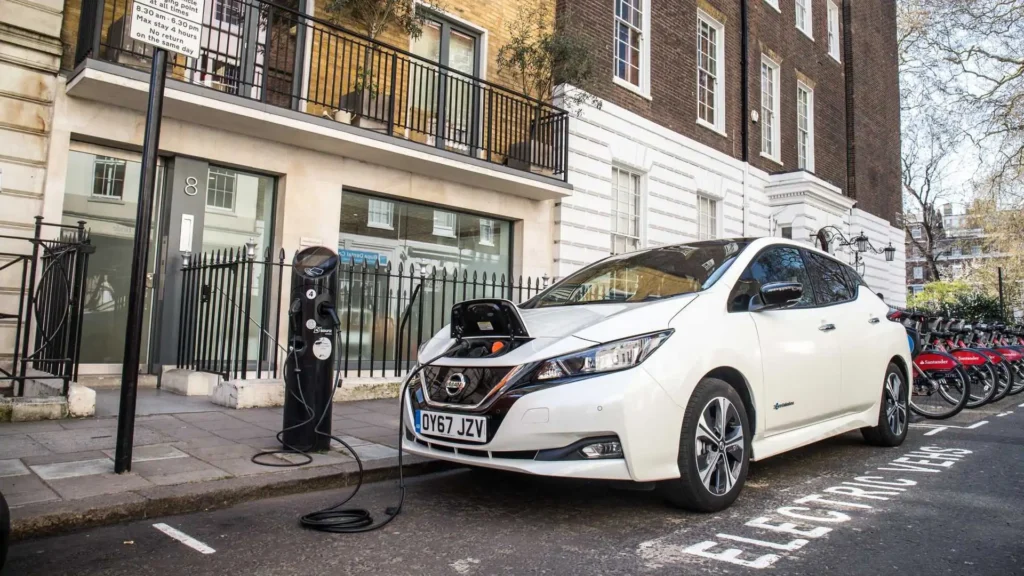
Level 2 charging is powered by a 240-volt source and can be found in residential household chargers, work environments, and public charging locations. Level 2 charging can produce 12 to 80 miles of range per hour, with capabilities varying with a car’s capacity and charger output. Most cars can be filled in 4 to 10 hours with Level 2 chargers, and Level 2 chargers make overnight at work and at home an efficient and convenient alternative for many owners. Level 2 chargers can even be installed in a car owner’s residence for assured daily use, and owners can have a car ready to go at a moment’s notice.
DC Fast Charging (Public Fast Charging Station
DC fast charging, Level 3 charging, is a lot faster than Level 1 and Level 2 charging alternatives. Fast chargers have high output, 50 kW to 350 kW, and can allow EVs to gain 100 to 200 miles of range in 15 to 30 minutes. Most chargers will charge a battery to 80% in 30–45 minutes, and then slow down charging to a level that will not overheat and age batteries. Fast chargers best serve long trips and can be placed at highway corridors and urban charging corridors. Not all EVs, nevertheless, can utilize most rapid charging, with a few having inbuilt charging limitations that will not permit them to utilize full power.
Ultra-Fast Charging (High-Power DC Charging)
Ultra-fast charging networks such as Tesla V3 Superchargers, Ionity, and Electrify America, and similar high-powered networks, deliver a number of the most rapid charging times available. All of these chargers range between 250 kW and 350 kW, and compatible EVs can gain a range of over 200 miles in under 15 minutes. Not all vehicles can use ultra-fast charging, however, because of battery limitations. These chargers, while effective for long highway driving, lack a presence in as many locations as Level 2 chargers, and use can at times be more costly.
Factors That Impact EV Charging Rate
Although the charger type is an important consideration, several additional factors will have an impact on how quick an EV can be refilled.
Battery Size and Charge Status
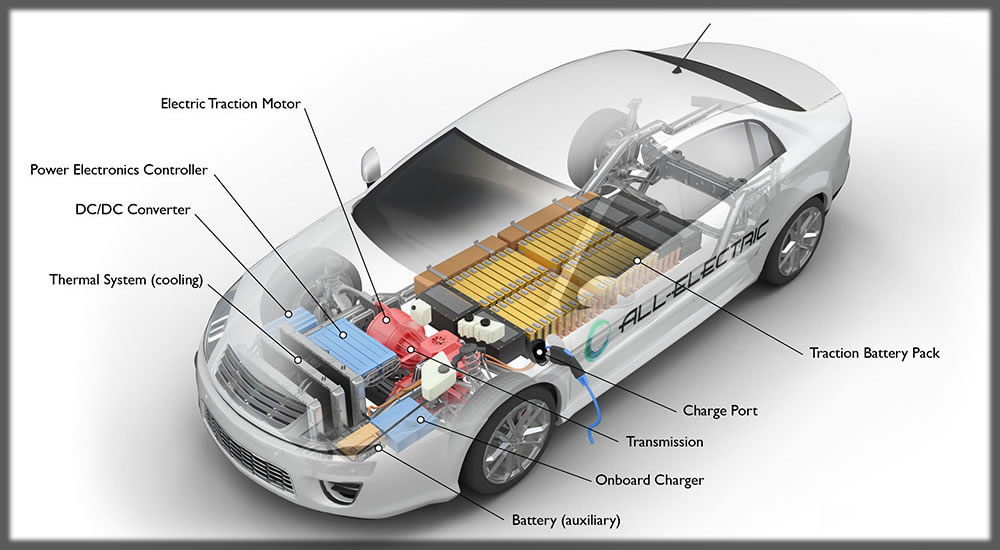
The capacity of the battery in an EV plays an important role in overall charging duration. It takes a long time to charge big batteries, and smaller batteries charge faster. In addition, charging, when completed to approximately 80% of capacity, also reduces in pace afterward to protect the battery from overheat and extend its life span.
Maximum Charge Capacity of the Car
Every electric vehicle has a charging capacity at its maximum point. Some cars, for example, will only accept a 50 kW charge even if a 350 kW charger is inserted. That limitation will imply despite ultra-fast chargers, not all vehicles will see lessened charging times. Efficient choice of charging stops can be made by owners with the knowledge of the car’s charging capacity.
Temperature and Weather Conditions
Environmental factors, in terms of extreme temperatures, can impact charging speed. Cold temperatures decelerate efficiency, and batteries charge at a lesser pace, while high temperatures can cause the battery’s cooling mechanism, and hinder the intake of power in a bid to cool down and not overheat. Moderate temperatures for charging will produce best charging speeds.
Type of Charging Cables and Infrastructure
The quality of charging infrastructure and cables is also a contributing factor in charging times. High-performance, high-quality cables and well-maintained charging infrastructure transmit efficient power, with less loss and optimized charging times. Poorer, older, and less efficient cables can result in slow charging and inefficient delivery of power.

Conclusion
The speed at which an EV will charge depends on a variety of factors, including the charger, car battery capacity, car charging capacity, and surrounding conditions. Level 1 charging is slow and best for overnight at-home charging, but Level 2 chargers have a preferable daily charging option. DC fast charging and ultra-fast charging have minimum recharging times and can best be utilized for extended trips, but depend on the car’s suitability for high powers to receive them. As battery and charger technology continues to advance, charge times will drop, and EV driving will become even easier. For owners who desire an optimized charging experience, it helps to understand options and charging velocities. Home, workplace, and highway charging can all benefit with a proper charger, keeping the car ready to go at any time. Do you have a request for recommendations for best home EV chargers and public charging networks in your region?