Why Are EVs So Expensive? Electric vehicle (EV) batteries are one of the most expensive components of an EV and contribute significantly to the final cost of the vehicle. While the cost of batteries has come down over the years, they remain expensive due to the expensive nature of raw materials, complex manufacturing processes, high research and development costs, and supply chain problems. A review of these factors provides insight into why EV batteries are expensive and how, in the future, they may be made more affordable.
Expensive Raw Materials
One of the most significant contributing factors to high EV battery expenses is high-value and restricted raw materials usage. High-value and restricted materials such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese, utilized in lithium-ion batteries, prevalent in EVs, not only have high extraction and processing expenses but have price fluctuations with restricted availability and growing demand globally. Despite lithium’s relatively high abundance, its extraction comes with high energy demand. Cobalt, one of the most expense-intensive materials in EV batteries, is concentrated in a narrow group of nations, and its availability is under political uncertainty. Nickel and manganese, both important for increased battery life and energy density, contribute to high production costs through mining and processing complications.
Complex and Costly Manufacturing Process
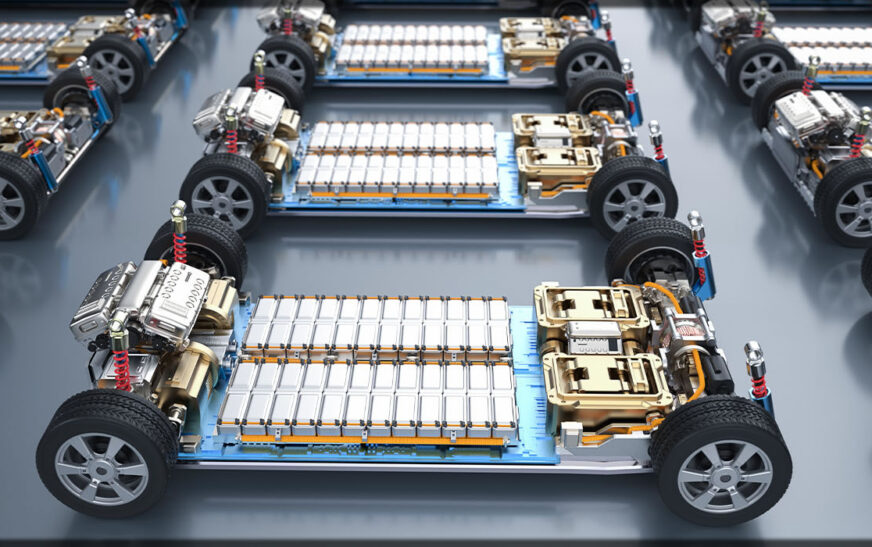
The manufacturing of EV batteries is a technology-intensive and complex one with significant investment in technology. There are numerous complex processes in producing batteries, including extraction, refinement, production of electrodes, production of cells, and assembling batteries in packs. All these processes entail high-tech tools, precision engineering, and cleanrooms, and hence become an expensive exercise. There is an additional cost in battery pack integration in terms of integration of coolers and management, apart from improving efficiency and security, for overall cost. In contrast to traditional car production, EV battery production requires new factories and high-tech workers and hence restricts expansion and price cutting at a slow pace.
High Research and Development Costs
Research and development (R&D) are also a key reason for high EV battery cost. The EV industry is growing rapidly, and companies invest a lot in R&D to develop battery technology, including energy density, charging times, and durability. Innovations such as solid-state batteries, high-speed charging technology, and environmentally friendly battery recycling technology require a lot of work, and therefore, drive batteries’ high price tag. Even though these innovations will in future make EV batteries cheaper and efficient, in current times, they drive them at a high price.
Limited Mass Production
Limited large-scale production is yet one of the cost factors for batteries. Even with increased production in batteries in recent years, it is not yet at a level with conventional gasoline-powered car production. It takes billions of dollars to establish gigafactories, and any form of disruption in the supply base can slow down production. Since battery production entails complex processes, any defects and efficiencies can result in significant financial loss, and hence, make it an expensive activity. Yet, with increased demand for EVs and increased production, battery prices will drop.
Geopolitical and Supply Chain Challenges
Supply chain factors and geopolitical factors also affect EV battery costs. Many of the materials essential to battery production are mined and processed in specific places, such as lithium in South America and cobalt in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Transporting these materials to where they are required costs money, and trade restrictions, import duties, or geopolitical uncertainty can only increase costs. Supply chain disruptions, such as those generated by the COVID-19 pandemic or conflicts in key mining regions, have also generated material shortages and price hikes. To mitigate these risks, the majority of automakers and governments are investing in local battery production, which should stabilize costs in the coming years.
Recycling and Costs of Sustainability
Recycling and sustainability programs contribute to high EV battery expenses, too. Even with new EV batteries having long lifespans, batteries will eventually degrade and have to be replaced or recycled over time. Recycling batteries is an expensive and complex process, with technology involved in extracting such high-value materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel. Others have started researching second-life use, with older EV batteries reused for energy storage systems, but re-packing and re-conditioning them is not cheap. Stringent environment legislation requires car companies to make investments in environmentally sound battery disposal and recycling programs, adding to overall expenses.
Will EV Battery Costs Decline?
Though EV batteries are costly at present, their price will fall in the future decade with improvements in technology and increased production capacity. Improved battery chemistry, including lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP) and solid-state batteries, can make them less costly by excluding high-cost materials such as cobalt. Greater factories and automation will make production less costly, and efficient recycling will reduce demand for freshly mined materials. Government subsidies and investments in domestic battery production will also make EV batteries less costly in future years.

Conclusion
EV batteries are costly, with high raw material expenses, sophisticated production processes, high investments in R&D, and supply chain issues contributing to them. Despite a slow but continuous price drop, EV batteries remain a significant proportion of an electric car’s overall price tag. Nevertheless, with continued technological improvements, economies of scale through increased production, and enhanced recycling, battery prices will fall, and EVs will become even more affordable for a larger group of buyers. As demand for EVs continues to rise, technological improvements in batteries will become increasingly important in driving down the price of electric cars and enhancing their viability in terms of both cost and sustainability.