How Electric Vehicle Charging Works: A Simple Guide. Electric vehicle (EV) charging is a key aspect of EV ownership, ensuring that drivers can power their vehicles conveniently and efficiently. Unlike gasoline-powered cars that require refueling at gas stations, EVs rely on electricity stored in batteries, which must be charged regularly. Understanding how EV charging works, the different charging levels, connector types, and charging station availability can help EV owners make informed decisions about maintaining their vehicles’ power needs.
Understanding EV Charging Basics
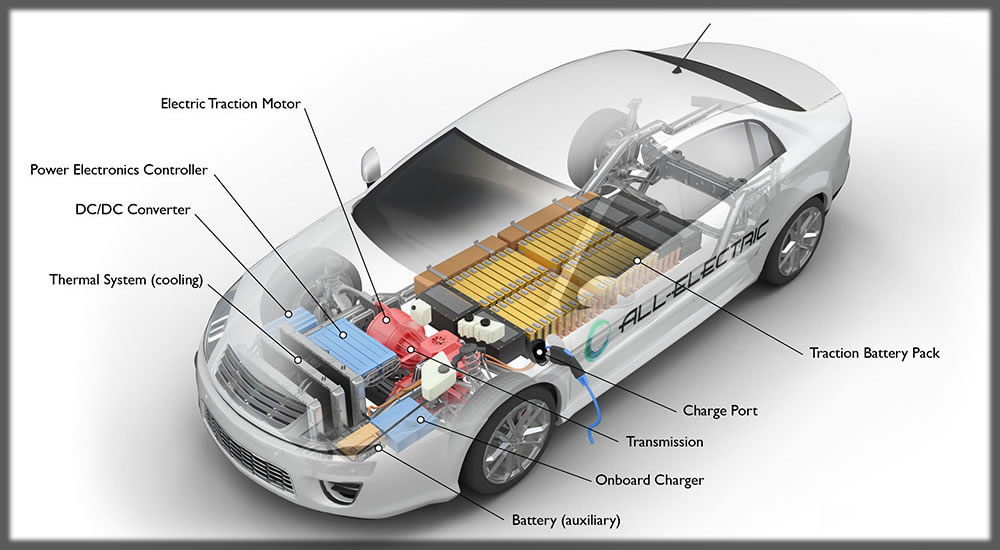
Electric vehicles use rechargeable lithium-ion batteries to store electricity, which powers the electric motor. Charging an EV involves transferring electricity from an external power source—such as a home charger or public charging station—into the vehicle’s battery. The time required to charge an EV depends on factors such as battery size, charging speed, and power output from the charging station.
Levels of EV Charging
There are three main levels of EV charging, each offering different speeds and power outputs:
Level 1 Charging (Slow Charging)
Level 1 charging is the most basic and slowest form of EV charging. It uses a standard 120-volt household outlet, making it the most accessible option for EV owners. Most EVs come with a Level 1 charging cable that can be plugged directly into a regular home socket. However, charging at this level is slow, typically providing only 2 to 5 miles of range per hour of charging. Fully charging an EV battery can take anywhere from 24 to 48 hours, making Level 1 charging more suitable for plug-in hybrid vehicles (PHEVs) or for those who drive short daily distances.
Level 2 Charging (Faster Home and Public Charging)
Level 2 charging is significantly faster and requires a 240-volt power source, similar to what large home appliances like dryers use. It is the most common type of charging for home installations and public charging stations. Level 2 chargers can add between 10 to 60 miles of range per hour, depending on the charger’s power output and the vehicle’s charging capabilities. Most EV owners install a dedicated Level 2 home charger to ensure faster and more efficient charging.
Public Level 2 chargers are widely available in shopping centers, workplaces, and parking lots, making them a convenient option for topping up an EV’s battery during the day. Installing a Level 2 charger at home usually requires professional installation and an upgraded electrical panel, but it significantly reduces charging time compared to Level 1 charging.
Level 3 Charging (DC Fast Charging)
Level 3 charging, also known as DC fast charging, is the fastest and most powerful charging option available for EVs. It uses direct current (DC) instead of alternating current (AC), allowing for much faster charging speeds. DC fast chargers can provide 60 to 300 miles of range in just 15 to 45 minutes, making them ideal for long road trips and highway stops.
However, not all EVs are compatible with DC fast charging, and frequent use can cause battery degradation over time. Additionally, Level 3 chargers are expensive to install and operate, so they are primarily found at commercial charging stations rather than home setups.
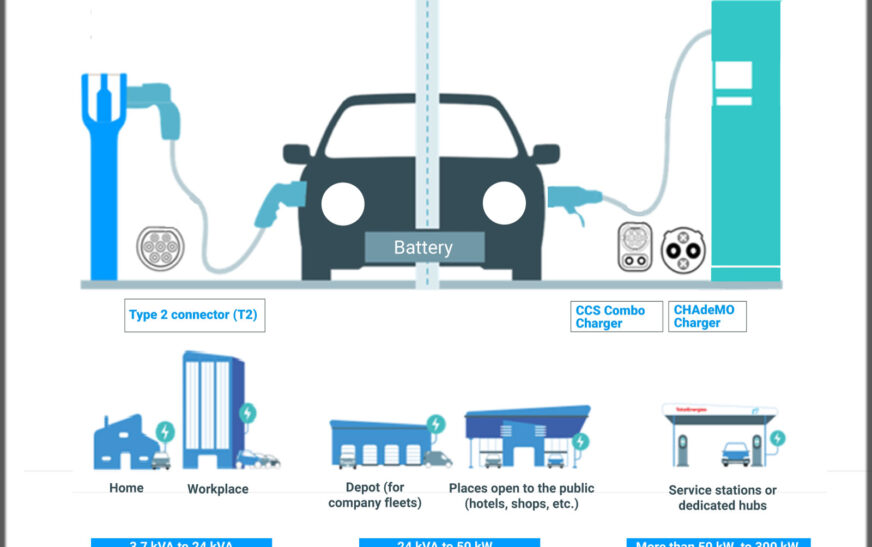
EV Charging Connectors and Compatibility
Different EV manufacturers use various charging connectors, so understanding which plug type is compatible with your vehicle is essential. The most common EV connectors include:
- J1772 Connector – Used for Level 1 and Level 2 charging in North America, compatible with most EVs except Tesla (which requires an adapter).
- CHAdeMO Connector – A fast-charging standard used by some older EV models, such as the Nissan Leaf.
- CCS (Combined Charging System) Connector – A widely used fast-charging connector that combines AC and DC charging capabilities, found on many EVs.
- Tesla Connector – Exclusive to Tesla vehicles, compatible with Tesla Superchargers, but adapters are available for other charging networks.
Home vs. Public Charging
EV owners can choose between charging their vehicles at home or using public charging stations.
Home Charging
Home charging is the most convenient and cost-effective option for most EV owners. With a Level 2 home charger, an EV can be fully charged overnight, ensuring it is ready for daily use. Many utilities offer incentives and rebates for installing home chargers, further reducing costs.
Public Charging
Public charging stations are essential for EV owners who travel long distances or do not have access to home charging. They are commonly found at shopping centers, office buildings, parking garages, and highway rest stops. Some charging networks require a membership or mobile app to access charging stations, while others allow for pay-as-you-go options. Popular public charging networks include Tesla Supercharger, Electrify America, ChargePoint, and EVgo.
Factors Affecting EV Charging Speed
Several factors influence how quickly an EV can charge, including:
- Battery Size – Larger batteries take longer to charge, but they also provide more range.
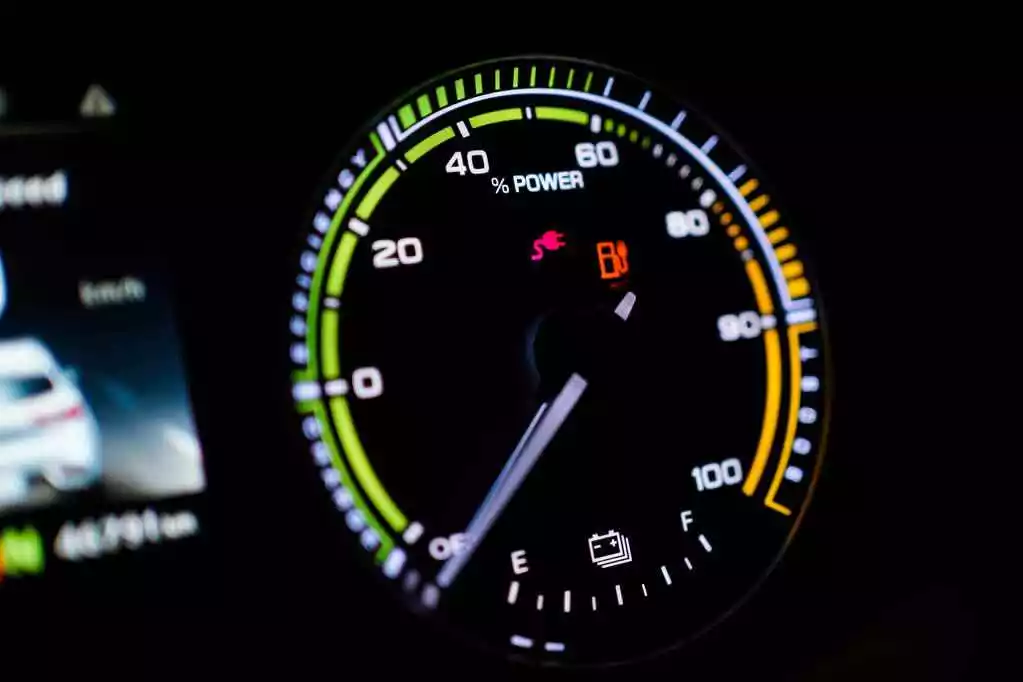
- State of Charge – Charging slows down as the battery approaches full capacity to prevent overheating and battery degradation.
- Charging Station Power Output – Higher-powered chargers deliver energy faster, reducing overall charging time.
- Vehicle Charging Capabilities – Some EVs support faster charging speeds than others, depending on their built-in charging technology.
Cost of EV Charging
The cost of charging an EV depends on where and how it is charged. Home charging is generally cheaper, especially if charged during off-peak hours when electricity rates are lower. Public charging stations vary in pricing, with some offering free charging while others charge per kilowatt-hour (kWh) or by time. DC fast charging is usually the most expensive option but provides rapid charging when needed.
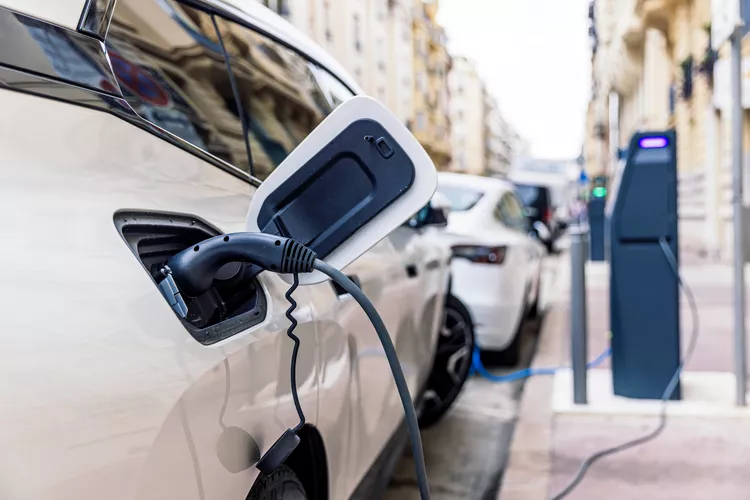

Conclusion
Understanding how EV charging works is essential for EV owners to ensure they can efficiently maintain their vehicle’s battery life and driving range. With different charging levels, connector types, and charging locations available, EV drivers have multiple options for keeping their vehicles powered. Whether charging at home overnight or using public charging stations on long trips, the growing EV infrastructure makes electric vehicle ownership more convenient than ever before.