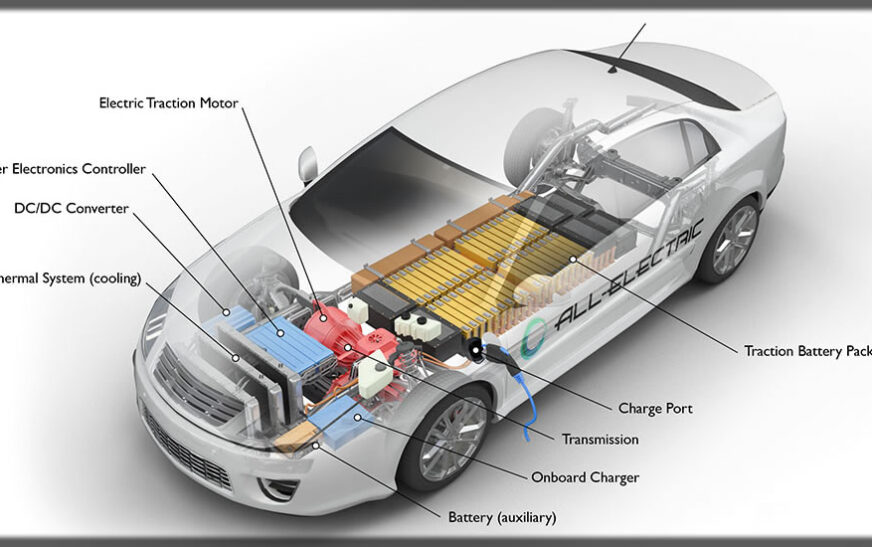
How to Install an Electric Car Charger at Home. As electric cars become increasingly popular, many EV owners prefer having a residential charging station for convenience, efficiency, and cost savings. With a residential EV charger, your car will charge a lot faster compared to a typical household outlet, keeping your car in its best form for your daily commute, weekend outings, and long trips. Installing a residential charging station takes careful planning and installation, including selecting an apt charger, inspecting your electrical system, and following proper installation procedures for security and compliance with your locality’s codes.
Choosing a Sufficient EV Charger
When installing an EV charger at your residence, your first consideration is selecting the proper charger. EV chargers can fall into three categories, with a range of charging capacities and requirements for power. Level 1 chargers use a 120V household outlet and have a 2-5 miles of range per hour charging capacity, and work best for overnight charging but not for daytime use. Level 2 chargers use a 240V outlet and work best for residential installation, with a much larger 10-60 miles of range per hour charging capacity. DC Fast Chargers cannot work in residential settings, with high requirements for power and installation cost, and can only be installed in public charging networks.
Assessing Your Electrical System
Before proceeding with installation, your home’s electrical system must be evaluated to confirm that it can support an EV charger’s increased demand. Check your electrical panel’s capacity, and confirm that it will have enough room for a 240V single-purpose circuit. Most Level 2 chargers utilize a 40-50 amp single-purpose circuit for effective use. In case your electrical panel isn’t capable, an upgrade will have to be conducted, and installation will become even more expense-intensive. Check your home’s breaker and wiring system to confirm compatibility with high-powered appliances. Have a qualified electrician evaluate your system to confirm whether any upgrades will have to be conducted first, in preparation for charger installation.
Selecting an Optimum Installation Position
The location of your EV charger is important in its ease and efficiency of use. Ideally, have your charger installed at your parking location to spare yourself long cords, which adds to installation costs. In choosing a location, have consideration for proximity to your electrical panel, weather protection, and multiple car access in case of urgency. In an outdoor installation, have your charger with a weatherproof enclosure to protect it from rain, snow, and extreme temperatures. Ensure your charging cable is long enough to comfortably extend to your EV’s charging socket.
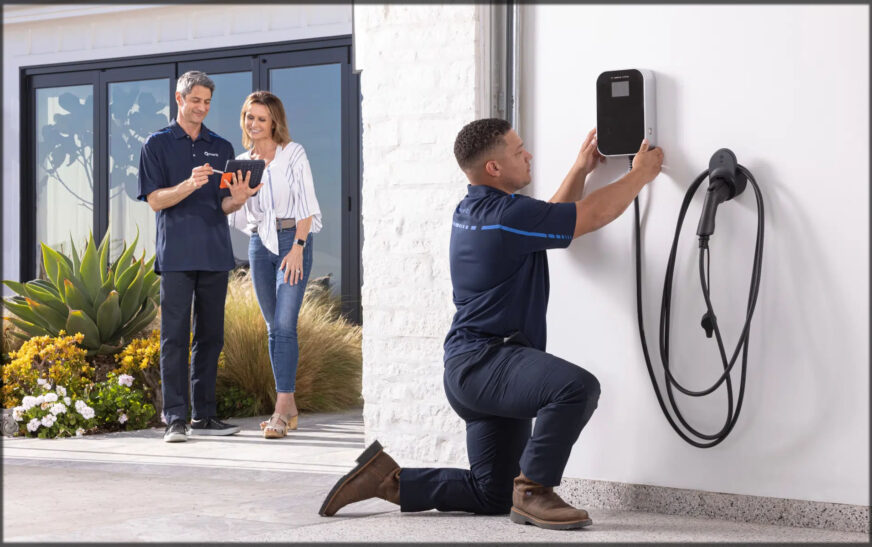
Hiring a Qualified Electrician for Installation
Although some homeowners with an electrical background will attempt a DIY installation, a certified electrician is ideal for installation for security and for adhering to electrical codes. A qualified electrician will undertake significant aspects of installation, such as installation of a 240V dedicated circuit, correct grounding, and adhering to the National Electrical Code (NEC) and your state and region codes and laws. They will secure permits and schedule inspections, possibly mandated by your state and city governments, in addition to taking care of significant aspects of the installation. Having a charger professionally installed will have your charger working effectively and safely and will save you any electrical risk.
Obtaining Permits and Inspection
Depending on your location, permits will first have to be purchased in preparation for having an EV charger installed. Permits and electrical inspections, in many instances, mandated by your local codes, will have to verify installation in compliance with compliance and safety requirements. Application with your local permit office, installation follow-up scheduling, and use approval, in most instances, will then follow. Having a qualified electrician will make it easier, and having an awareness of your local codes and requirements will make them easier to work through.
Installation Procedure
Once you have bought your charger, analyzed your electrical system, and have any permits, installation proper can start. The installation will then follow these critical phases:
1. Turn off power– As a precaution, power to the breaker panel is first shut off when any work with electricity is started.
2. Install a 240-Volt Outlet or Hard Wired Connection – Certain chargers will demand a 240-Volt outlet, and others will demand a direct, hard-wired, connection to your electrical panel.
3. Mounting of Charging Unit – Mounting of charger firmly onto a mounting post or a wall and it should ideally be placed in a secure and accessible position.
4. Run Electric Cables – An electrician runs proper wires, with proper grounding and overvoltage protection for safeguarding electrical faults.
5. Test the System – Once installed, then, the charger will then be subjected to testing by an electrician to confirm power flow, connectivity, and overall functionality
Setting and Installing an Electric Car Charger at Home
After installation, follow through with configuring your charger for use in a routine manner. Most new EV chargers include smart capabilities, including connectivity through Wi-Fi and smartphone applications that allow you to monitor and schedule charging sessions. Set settings to take advantage of off-peak pricing for electricity and save utility dollars. To charge, simply plug in your EV, verify your charger is operational, and allow it to charge your battery about your driving schedule.
Understanding Costs and Incentives
The total cost of installation for a Level 2 residential charger is between $500 and $2,000, with installation cost variable according to equipment, electrician, and any electrical upgrade necessity. Government incentives, electric utility rebates, and federal tax credits can, nevertheless, pay for part of these expenses. Most areas have financial incentives for residential installation of EV chargers to make alternative transportation a reality. Check with your locality for any rebates and discounts for which you can apply, and make your purchase knowing part of your cost will be taken care of.
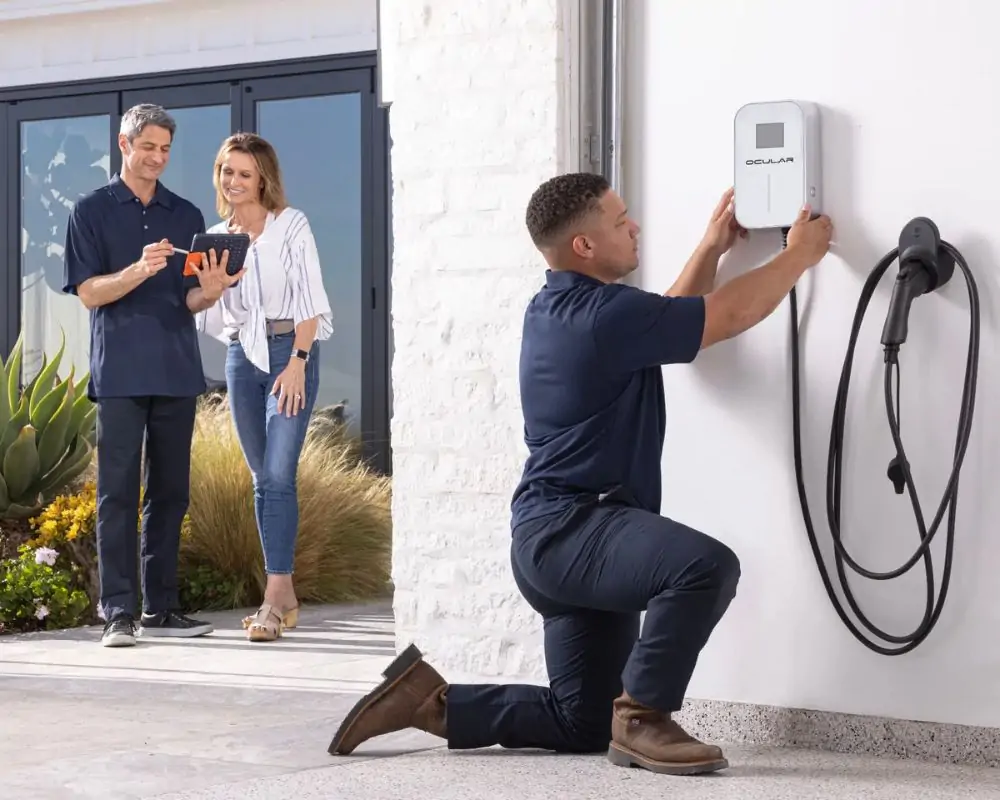

Conclusion
Installing an EV charger at your home brings unparalleled comfort, with overnight charging and less need for constant trips to public charging points. With careful planning, selecting an apt charger, inspecting your home’s electrical infrastructure, and following proper installation, one can have a safe and efficient installation. With high initial outlays, it can become unaffordable, but incentives and future savings in terms of fuel costs make in-house charging a wise investment. With careful planning and expert consultation, with a little planning, and expert consultation, one can have the comfort of rapid, efficient EV charging at one’s doorstep.