Beginner’s Guide to Understanding EV Battery Technology. Electric vehicles (EVs) are transforming the automotive industry with a cleaner, environmentally friendly alternative by offering conventional gasoline-powered automobiles. Behind every single EV stands its battery, and it is responsible for the air’s range, performance, and efficiency overall. In this article, we will simplify overall efficiency stand the basic technology of EVs and the future in terms of its development future
What is an EV Battery?
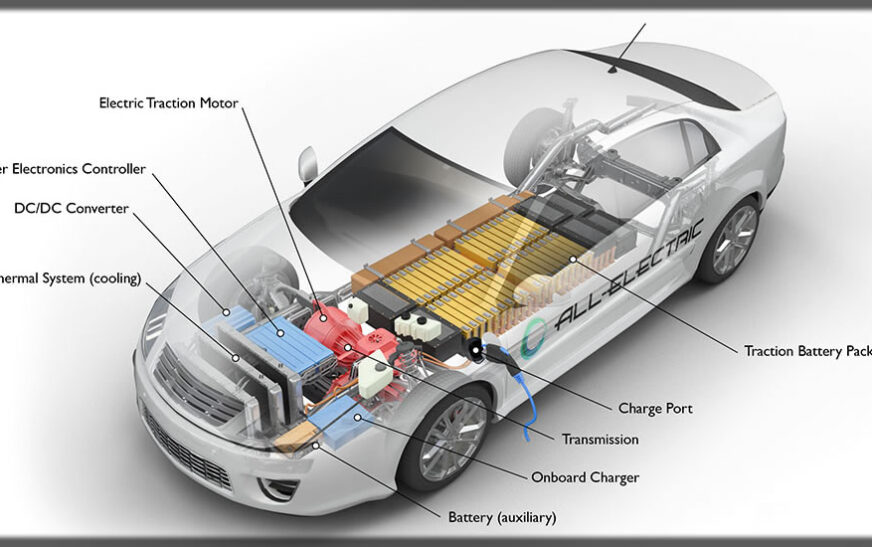
An EV battery is a battery-powered unit for storing energy that powers an electric car’s motor. In contrast to traditional ICE automobiles, fueled with gasoline or diesel, EVs run with stored electricity in batteries to drive a car. Most in current use in EVs is the lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery for its high density, efficiency, and long life span.
How Do Electric Car Batteries Work?
EV batteries function by storing electrical energy and then discharging it when it is needed to power the electric motor. Here is a basic rundown of how:
1. Charging: Charging is achieved when a car is plugged into a source of electricity. A charger converts AC current from a grid to DC current, which is stored in battery cells.
2. Energy Storage: Energy is stored in a chemical form in lithium-ion cells in a battery.
3. Powering the Motor: As one accelerates, stored battery energy is drained in terms of electrical current, energizing the motor and moving the car.which energizes moves
4. Regenerative Braking: During deceleration, the electric motor acts as a generator, and kinetic energy is recovered and recharged in a battery, with efficiency increased.
Types of EV batteries
Several types of batteries are used in electric vehicles, each with unique characteristics:
1. Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) Batteries
– The most common one in use in modern EVs.
– High density, long life, and lightweight
– Efficient and rapid charging capabilities
– Expensive but becoming more affordable with advancements in technology.
2. Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries
– Found in a few hybrid electric cars (HEVs).
– Longer lifespan than lead-acid batteries but lower energy density than Li-ion.
– Higher cost and less efficient recharging
– Less common in newer full EVs
3. Next-Generation Tech: Solid-State Batteries
– Expected to serve as a future alternative for lithium-ion batteries
– Higher density, increased charging, and heightened security
– Still in development stage but with high potential.
– Longer life and thermal stability
Battery life and range
The performance of an EV battery is rated in kilowatt-hours (kWh), and it reflects how much energy it can store. A larger rating in terms of kWh tends to mean:
– Longer driving distance between recharging
– More acceleration and high-speed driving performance at your fingertips.
– Heavier and more expensive battery packs
For example, a Tesla Model 3 comes with a battery range of 50 kWh to 82 kWh and an estimated range of 250 to 350 miles per charge. Luxury EVs, such as the Lucid Air, have over 100 kWh battery capacities and over 500 miles range per charge.
Charging EV Batteries
EVs can be refuelled with a range of types of refuelers:
1. Level 1 Charging (Slow Charging
– Uses a standard 120V residential outlet.
– Adds 2-5 miles of range per hour
– Best for overnight at home but not for long trips
2. Level 2 Charging (Fast Home & Public Charging)
– Uses a 240-volt outlet, for example, an electric clothes dryer
– Adds 10-60 miles of range per hour
– Common in residential, commercial, and public charging spaces
3. Fast Charging (Quick Charging)
– Uses high voltage direct current for quick charging.
– Adds up to 80% charge in 30-60 minutes.
– Found at highway stops and public charging terminals.
– Ideal for long-distance trips
4. Wireless Charging (NextGen Tech)
– Uses electromagnetic waves to transmit energy wirelessly.
– Eliminates the use of plug and cable requirements.
– Still in its infancy stage but soon to go widespread
Battery life and degradation
EV batteries won’t ever last but will have a life of 8-15 years or 100,000 to 300,000 miles with a considerable loss in capacity. What can affect battery life?
– Charging behaviour : Frequent rapid charging can cause acceleration of degradation.
– Extreme temperatures : High temperatures and extreme cold will impact battery performance.
– Driving behaviour : Harassing driving will drain a battery life and make it less efficient
– Battery coolers : Electric automobiles with high-tech thermal management have batteries with a long life span.
Recycling and Sustainability
As EVs gain widespread acceptance, reuse and sustainability of batteries have become critical concerns. Reused EV batteries can:
1. Recycled: Materials including lithium, cobalt, and nickel can be recycled and reused.
2. Repurposed: Home and commercial structures can use recycled EV batteries for storing energy.
3. Disposed Properly: Manufacturers are developing eco-friendly disposal methods to minimize environmental impact.
Innovations in battery recycling work towards creating a looped system under which recovered materials in recycled batteries will contribute towards creating new batteries, minimizing raw material mining.
The Next Wave in EV Battery Tech The EV sector keeps developing to enhance battery performance, price, and environmentally friendly performance.
Emerging future improvements include: –
Solid-State Batteries : With high energy density, high charging, and increased security
Faster Charging Technology: Charging in a matter of minutes, not hours
Improved Recycling Methods: Reduced consumption and increased efficiency in critical minerals
Alternative Chemistries for Batteries: Sodium-ion and graphene batteries for less environmentally friendly and less expensive alternatives.
Battery-as-a-Service (BaaS): Users can swap out, or even rent, batteries, cutting down on initial EV purchase price.
Wireless and Dynamic Charging: Techniques allowing EVs to charge when parked, and even when in motion over specially designed highways.

Conclusion
Understanding EV battery technology is important for anyone contemplating an electric car. As technology in charging infrastructure, energy storage, and sustainability keeps improving, EV batteries will become even more efficient, affordable, and environmentally friendly. With continued development, transportation’s future is increasingly electric, with long life, rapid charging, and cleaner batteries in its future.